Redis Integration
Track Redis performance and health metrics (commands/sec, CPU, memory, keyspace, replication, I/O) in Middleware.
Prerequisites
- Install the Middleware Host/Infra Agent on the machine that will collect metrics.
Setup
1 Create Database Credentials
Put your connection details in a YAML file (adjust host/port, auth, and TLS as needed):
# /home/ubuntu/redis-creds.yaml
redis:
endpoint: localhost:7379
## all fields below are optional ##
password: redis
transport: tcp ## tcp or Unix
tls:
- insecure: true
- ca_file: <path_to_certificate>
- cert_file: <path_to_certificate>
- key_file: <path_to_file>Docker Agents look for this file inside /var/log on the Agent host.
A quick reachability check helps before enabling the integration:
# Plain TCP
redis-cli -h <redis-host> -p 7379 PING
# TLS (example using a CA file)
redis-cli --tls -h <redis-host> -p 7379 --cacert <path_to_certificate> PINGExpect PONG if the server is reachable and the credentials/certs are valid.
2 Access Integrations
In Middleware, open Installations → All Integrations → Redis.
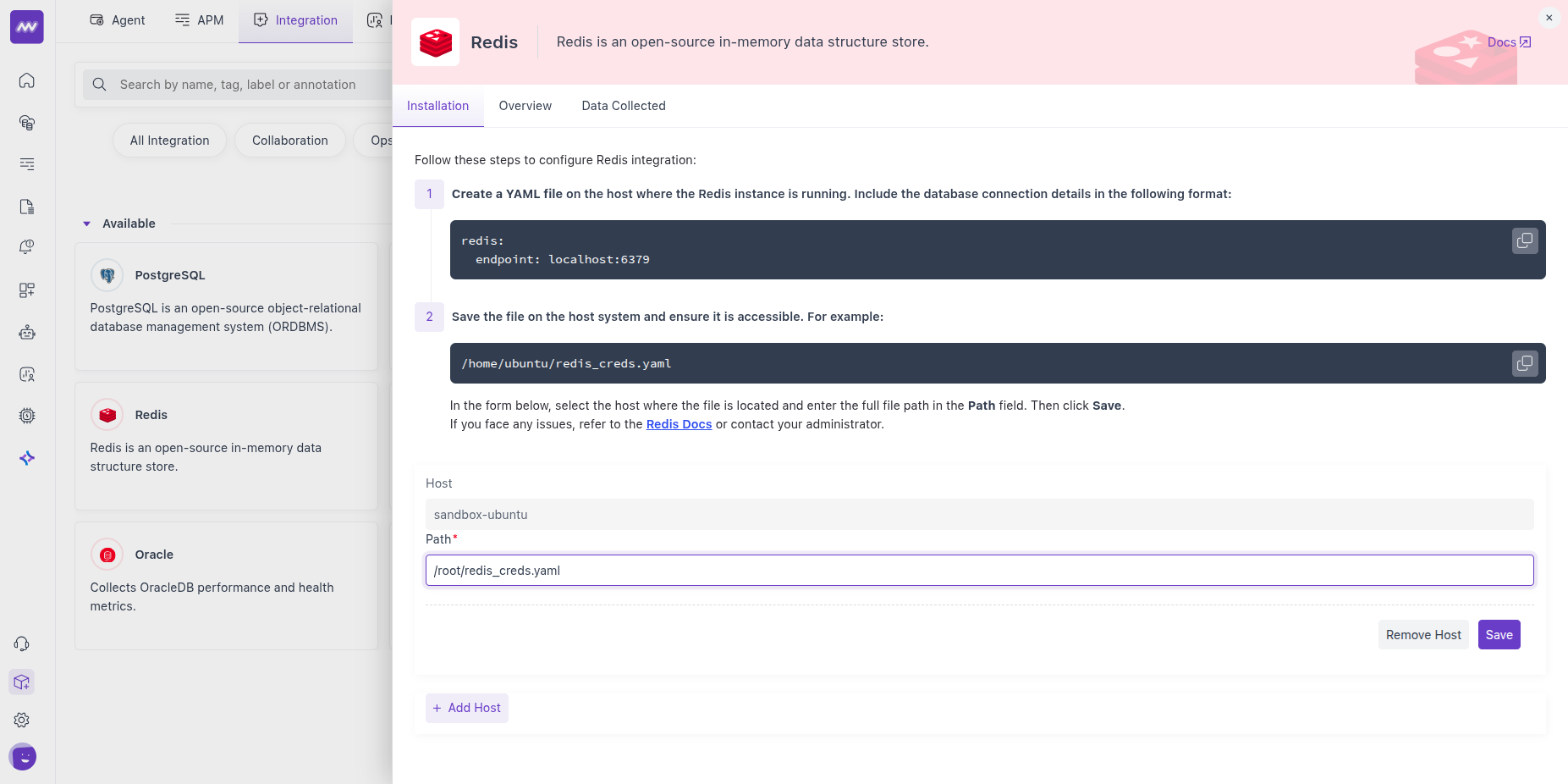
3 Enable Integration
Pick the host (where the Agent runs), enter the credential file path from Step 1, and Save.
Visualize Analytics
- A default Redis dashboard appears in Dashboard Builder after setup.
- To add custom charts, choose Add New Widget →
redisto browse available metrics.
Alerts
Create alerts on any Redis metric: choose Detection Method: Database, Database Type: Redis, pick a metric, and set your conditions.
Metrics Collected
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
redis.maxmemory | Configured maxmemory value |
redis.role | Node’s role |
redis.cmd.calls | Total number of calls for a command |
redis.cmd.usec | Total time for all executions of this command |
redis.uptime | Number of seconds since server start |
redis.cpu.time | System CPU consumed since start |
redis.clients.connected | Client connections (excludes replica connections) |
redis.clients.max_input_buffer | Largest input buffer among current clients |
redis.clients.max_output_buffer | Longest output list among current clients |
redis.clients.blocked | Clients pending a blocking call |
redis.keys.expired | Total key expiration events |
redis.keys.evicted | Keys evicted due to maxmemory |
redis.connections.received | Connections accepted by the server |
redis.connections.rejected | Connections rejected due to maxclients |
redis.memory.used | Total bytes allocated by Redis |
redis.memory.peak | Historical max bytes consumed by Redis |
redis.memory.rss | Bytes allocated from operating system |
redis.memory.lua | Bytes used by the Lua engine |
redis.memory.fragmentation_ratio | Ratio between memory.rss and memory.used |
redis.rdb.changes_since_last_save | Number of changes since latest dump |
redis.commands | Number of commands processed per second |
redis.commands.processed | Total commands processed |
redis.net.input | Bytes read from the network |
redis.net.output | Bytes written to the network |
redis.keyspace.hits | Successful key lookups |
redis.keyspace.misses | Unsuccessful key lookups |
redis.latest_fork | Duration of latest fork (µs) |
redis.slaves.connected | Number of connected replicas |
redis.replication.backlog_first_byte_offset | Master offset of the replication backlog buffer |
redis.replication.offset | Current replication offset |
redis.db.keys | Number of keyspace keys |
redis.db.expires | Keys with expiration |
redis.db.avg_ttl | Average key TTL |
Troubleshooting
- Integrations menu is missing: Ask an admin to grant your role Installation permissions in Settings.
- Agent can’t reach Redis: Test from the Agent host:
redis-cli -h <host> -p <port> PING(or add--tls --cacert <ca>for TLS). You should getPONG. Fix DNS/firewall/port or credentials if it fails. - Authentication errors: Supply the password with
-aorREDISCLI_AUTHand retry the probe:REDISCLI_AUTH='<pass>' redis-cli -h <host> -p <port> PING. - TLS handshake fails: Verify CA/cert/key paths and server certificate trust; retry with correct
--cacert(avoid--insecureexcept for quick tests). - Clustered/replicated setups show only one node: Add each node you want monitored (metrics are per instance/endpoint). You can sanity-check per node with
redis-cli INFOor sectioned calls likeINFO replication.
Need assistance or want to learn more about Middleware? Contact our support team at [email protected] or join our Slack channel.